Getting Started with Enterprise Resource Planning Systems
Introduction to ERP Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are powerful tools used by companies of all sizes to manage their operations and keep track of financial information. ERP systems provide businesses with an integrated view of their entire organization and enable them to make decisions quickly, efficiently, and accurately. They also help streamline processes, improve customer service, reduce costs, and increase efficiency.
An ERP system is a suite of business applications that use a common database to store data. This allows for better integration across different areas of the business such as finance, operations, sales & marketing, etc., enabling the user to access the same data from multiple sources without having to manually enter it multiple times. ERP systems are typically made up of separate modules that can be customized based on specific needs or requirements within an organization. Common modules include accounting & finance (A/R & A/P), inventory control & tracking (warehouse management), human resources management (HRM), customer relationship management (CRM) as well as other specialized tools for healthcare organizations or retail stores, etc.
An ERP system in Singapore can help businesses stay ahead of the competition by providing real-time insights into critical business information and processes. With an ERP system, businesses can manage their inventory, track customer orders, and optimize their supply chain—all in one system.
The primary benefit associated with implementing an ERP system is improved visibility into operations across departments in order to make more informed decisions faster than ever before.
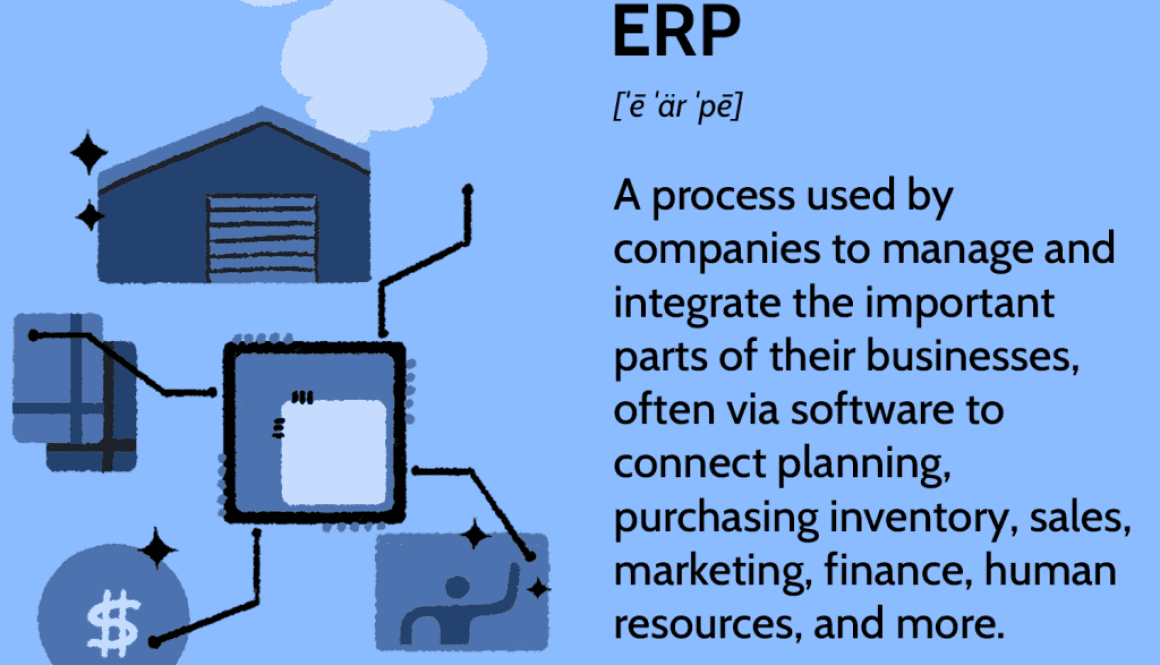
Definition of ERP
The term Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is used to describe the practice of utilizing a system of integrated applications to manage the business processes of an organization. An ERP system aims to provide visibility and control over all essential functions and processes within a company. This allows organizations to have improved data accuracy, increased efficiency, and better decision-making capabilities.
An ERP system typically consists of software modules that cover various aspects of an organization’s operations such as accounting, inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), human resources (HR), and supply chain management. Each module is tailored for a specific purpose within the overall system, but they are all connected together in order to provide real-time information throughout the organization. The goal is for all departments within an organization to share data across multiple locations while also providing greater visibility into how each department affects other departments or business activities as well as offering insight into potential areas for improvement.
Benefits of ERP Systems
The modern business world is highly competitive and organizations are constantly looking for ways to optimize their processes and stay ahead of the competition. One of the best tools to achieve this goal is an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system. ERP systems have become increasingly popular in recent years due to the many benefits they offer businesses, including increased efficiency, improved customer service, streamlined operations, and greater visibility into operations.
First and foremost, ERP systems help businesses save time by automating processes such as data entry, workflow management, accounting tasks, inventory management, and reporting. This means that organizations can focus less on mundane tasks and more on strategic planning or innovation. Streamlining these processes across departments with a unified system of record-keeping organizations can save time while also reducing errors resulting from manual data entry or incorrect calculations.
Another key benefit of implementing an ERP system is improved customer service levels as customers’ orders can be tracked much more efficiently than before. This helps ensure that orders are fulfilled in a timely manner so customers’ expectations are met or exceeded every time they do business with your company.
Components of an ERP System
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are powerful business solutions that integrate many departments and functions of a business into one cohesive system. With its ability to bring together multiple areas of an organization, ERP systems can be invaluable for businesses looking to increase efficiency and profitability.
An ERP system is made up of several components that work together to streamline and automate the different processes within a company. These components include modules for financial management, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), analytics & reporting, inventory control, and more.
Financial Management: This module helps manage the finances of an organization including accounts payable/receivable, budgeting & forecasting as well as financial reporting. It provides accurate data on cash flow and liquidity while allowing businesses to stay on top of their budgets and minimize risks associated with financial decisions.
Human Resources: This module helps manage HR processes such as employee data entry & maintenance, payroll processing & accounting services as well as performance reviews & development planning tools. It makes it easier for companies to track employee information in one place while also providing insights into how best to utilize their workforce.
Manufacturing: The manufacturing module provides visibility into production operations by tracking materials used in production runs or assembly.
Types of ERP Software
In today’s digital world, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a must-have for businesses of all sizes. ERP software helps to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and provide better customer service. With so many different types of ERP software available, it can be difficult to decide which one is right for your business. To help you make an informed decision, here’s a look at the different types of ERP software available on the market today.
The first type of ERP software is known as “vertical-specific” or “industry-specific” solutions. This type of system focuses on providing tools tailored specifically to a certain industry or sector (such as banking or healthcare). These systems are designed with features that are best suited to meet the needs of that specific industry and can provide powerful insights into operations within that sector. However, these systems tend to have higher implementation costs since they require more customization than other types of ERP solutions.
The second type is known as “general purpose” solutions which are not tailored towards any particular industry but rather focus on providing generic functionality across multiple industries and sectors such as accounting, supply chain management, and customer relationship management (CRM).
Challenges and Limitations of Implementing an ERP System
Introduction
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems have become a key technology for businesses of all sizes to manage their operations. With the ability to integrate data from multiple sources into a single, unified system, ERP can provide businesses with increased efficiency and cost savings. However, implementing an ERP system is not without its own set of challenges and limitations.
Challenges
One of the biggest challenges when implementing an ERP system is ensuring that all aspects of the business are integrated into the new system. This includes data integration from existing legacy systems, customization to fit specific organizational needs, and training staff on how to use it effectively. Additionally, there may be resistance from employees who are used to working with existing systems or processes that may need to be changed or replaced as part of the implementation process.
Another challenge is managing costs associated with the implementation and ongoing maintenance of an ERP system. While there are cost savings associated with improved efficiency after implementation, up-front expenses can be costly depending on how complex or customized your solution needs to be in order for it to work properly within your organization’s infrastructure. Additionally, staffing requirements in terms of resources needed for installation and maintenance can add additional costs over time if not planned for correctly during the initial.
Conclusion
An ERP system is a powerful tool that can be used to streamline business operations and boost productivity. Its benefits include improved data sharing, reduced costs, increased efficiency, and improved accuracy of decision-making. By integrating all departments into a single system, ERP systems allow organizations to manage their resources more efficiently and with greater visibility. Ultimately, an ERP system can help businesses to reduce costs and increase profits by helping them better manage their operations.
Also Read : https://migatrendz.com/